 VDI
VDI
 VDI bindings
VDI bindings
 Output functions
Output functions
This library contains functions that allow the setting of
certain attributes. The following categories are available for this:
Note: The attributes set here are valid for a single
workstation, and retain their validity until the program terminates,
or the attributes are reset elsewhere.
See also: VDI workstations Style guidelines
Note: The attributes set here are valid for a single
workstation, and retain their validity until the program terminates,
or the attributes are reset elsewhere.
See also:
VDI workstations Style guidelines VDI fundamentals
This group of functions enables various attributes for the
filling of areas to be manipulated. The following routines are
available for this purpose:
The attributes set here are valid for a single workstation, and
retain their validity until the program terminates, or the attributes
are reset elsewhere.
See also:
VDI workstations Fill-type and pattern index Style guidelines VDI fundamentals
This group of functions enables various attributes for the
drawing of lines to be manipulated. The following routines are
available for this purpose:
The attributes set here are valid for a single workstation, and
retain their validity until the program terminates, or the attributes
are reset elsewhere.
See also:
VDI workstations Style guidelines
This group of functions enables various attributes for the
drawing of markers to be manipulated. The following routines are
available for this purpose:
The attributes set here are valid for a single workstation, and
retain their validity until the program terminates, or the attributes
are reset elsewhere.
See also: VDI workstations Style guidelines
This group of functions enables various attributes for the
handling of text to be manipulated. The following routines are
available for this purpose:
The attributes set here are valid for a single workstation, and
retain their validity until the program terminates, or the attributes
are reset elsewhere.
See also: VDI workstations Style guidelines
This group of functions permits setting of the writing mode as well as
the intenstity of a colour; it encompasses the following routines:
The attributes set here are valid for a single workstation, and
retain their validity until the program terminates, or the attributes
are reset elsewhere.
See also: VDI workstations Style guidelines
| Name: |
»Set Background Color«
|
| Opcode: |
201 (sub-opcode 4)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsr_bg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
This function sets the background colour for bitmaps.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY der Hintergrundfarbe
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
As of NVDI 5.00
|
| Group: |
Bitmap attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set Foreground Color«
|
| Opcode: |
200 (Sub-Opcode 4)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsr_fg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
This function sets the foreground colour for bitmaps.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY of the foreground colour
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
As of NVDI 5.00.
|
| Group: |
Bitmap attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
The following illustration shows the possible combinations of
the fill-type and the pattern index. The first number here specifies
the fill-type (blank (0), pattern (2) or hatching (3)), the second the
index of the fill-pattern or hatching style.
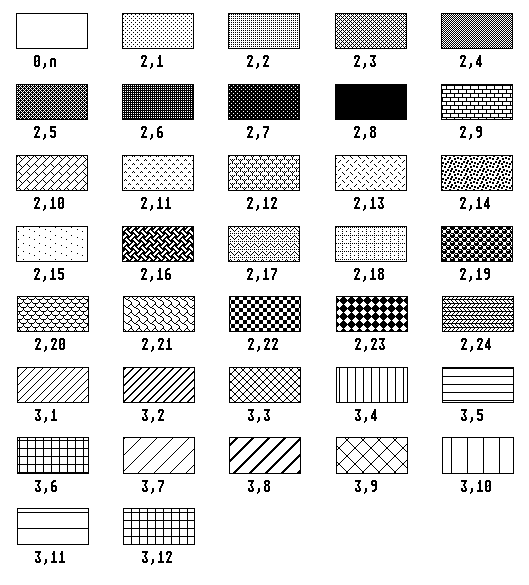
Note: A fill-type with the value 1 followed by any
hatching index always corresponds to fill-type 2 with hatching index 8
(solid). Index 1 for patterns of type 2 is always the pattern with the
lowest intensity on the relevant output device, and in addition always
in monochrome.
See also: vsf_interior vsf_style
Replace: In this mode the VDI overwrites the
background with the foreground colour in places where the
corresponding bit is set, or with the colour white if the
corresponding bit has the value 0. The logical combination is as
follows:
New := (foreground AND mask) OR (background AND NOT mask)
If we look at this in terms of working with pencil and paper,
one can imagine this as follows: First one draws a figure on white
paper, cuts it out and then sticks it over the graphic.
Transparent: In this mode, all bits of the figure to be
drawn that have the value 0 (i.e. are not set) are ignored by the
VDI. So only those bits are output that are set. The logical
combination in this case is as follows:
New := (foreground AND mask ) OR (colour AND NOT mask)
Here again a comparison of working with pencil and paper: This
mode corresponds to the Replace mode, only one is not drawing on
normal paper but on transparent foil.
XOR: In this mode all bits of the background and the
figure to be drawn are combined with an exclusive-OR (XOR), which
shows a useful and interesting feature:
If the same figure is drawn a second time in this mode, then it
will suddenly disappear again. Reason: An XOR combination of a bit
with itself always results in the inverses value. This is why this
mode is well suited for simple animations like a rubber box; the
recipe for this is as follows:
| 1. |
Output the object once
|
| 2. |
Output the object again (it has now disappeared again)
|
| 3. |
Alter the size or position of the object
|
| 4. |
Back to step 1
|
The logical combination here is: New := (mask XOR colour)
Im allgemeinen läßt sich über diesen Modus nur aussagen, daß
aus der Farbe Schwarz die Farbe Weiß wird, und umgekehrt; alles
andere ist nicht fest definiert.
Reverse transparent: In this mode, only those pixels are
taken into account which are set to the value 0 in the figure to be
drawn. The logical combination in this case is:
New := (colour AND mask) OR (foreground AND NOT mask)
This mode too offers some interesting application
ppossibilities; thus it can be used together with Transparent mode,
for instance, to let text appear with an additional background colour.
The following illustration should clarify the VDI writing
modes:
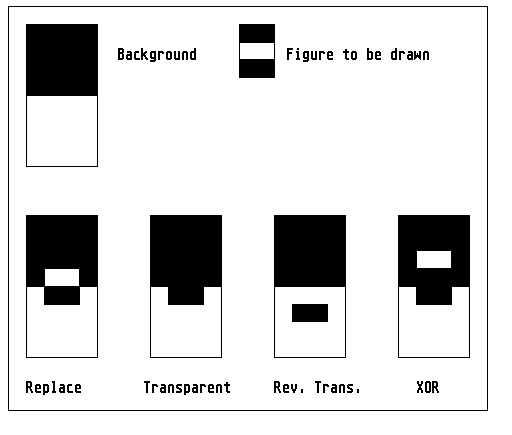
See also: vswr_mode
| Name: |
»Set Background Color« - Set the background colour for
objects
|
| Opcode: |
201 (Sub-Opcode 1)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsf_bg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
The call vsf_bg_color sets the background colour for drawn
objects.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY of the background colour
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
As of NVDI 5.00.
|
| Group: |
Fill attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set fill colour index« - Set the colour with which a
2-dimensional graphic object is to be filled.
|
| Opcode: |
25
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsf_color ( int16_t handle, int16_t color_index );
|
| Description: |
The call vsf_color sets the fill colour for 2-dimensional
graphic objects.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_index |
Requested fill color index
|
Note: The colour indices 0 and 1 are always available;
all others depend on the output device being used. An invalid colour
index will be replaced by the value 1. The colour index has no effect
on multicoloured patterns; it should be set to 1 in this case.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the actual colour set.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Fill attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_fillarea v_contourfill vr_recfl v_bar
v_pieslice v_circle v_ellipse v_ellpie v_rfbox vsf_udpat
|
| Name: |
»Set foreground colour« - Set the foreground colour for a
filled object.
|
| Opcode: |
200 (Sub-Opcode 1)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsf_fg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
This function sets the foreground colour for a filled
2-dimensional graphic object.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY of the foreground colour
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
As of NVDI 5.00.
|
| Group: |
Fill attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set fill interior style« - Set the fill-pattern type.
|
| Opcode: |
23
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsf_interior ( int16_t handle, int16_t style );
|
| Description: |
This function selects the fill-pattern type for a filled
2-dimensional graphic object.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| style |
Requested fill type
| 0 = |
Hollow
|
| 1 = |
Solid
|
| 2 = |
Pattern
|
| 3 = |
Hatch
|
| 4 = |
User-defined style
|
|
Note: If the requested type is invalid, type 0 (hollow)
will be selected.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the fill-type actually selected.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Fill attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_fillarea v_contourfill vr_recfl v_bar
v_pieslice v_circle v_ellipse v_ellpie v_rfbox vsf_style
vsf_udpat
|
| Name: |
»Set fill perimeter visibility« - Determine whether an
outline is to be drawn around filled areas.
|
| Opcode: |
104
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsf_perimeter ( int16_t handle, int16_t per_vis );
|
| Description: |
This function turns the outline border of a filled area
(rectangle, polygon, ellipse, ...) on or off.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| per_vis |
Visibility flag:
| 0 = |
Invisible
|
| <> 0 = |
Visible
|
|
Note: With outlining activated (default), the border
will be drawn in the current fill colour and as a continuous line.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the mode actually set.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Fill attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vsf_xperimeter v_fillarea v_contourfill vr_recfl
v_bar v_pieslice v_circle v_ellipse v_ellpie v_rfbox
|
| Name: |
»Set fill style index« - Set the fill-pattern.
|
| Opcode: |
24
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsf_style ( int16_t handle, int16_t style_index );
|
| Description: |
The call vsf_style determines the fill-pattern. The following
apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| style_index |
Index
|
Note: The function can only be used sensibly when the
fill type was not chosen as empty, opaque or user-defined.
Unavailable indices are replaced by pattern index 1.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the fill-pattern actually set.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Fill attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_fillarea v_contourfill vr_recfl v_bar
v_pieslice v_circle v_ellipse v_ellpie v_rfbox vsf_interior
|
| Name: |
»Set user-defined fill-pattern« - Define a new fill-pattern.
|
| Opcode: |
112
|
| Syntax: |
void vsf_udpat ( int16_t handle, int16_t *pfill_pat, int16_t
planes );
|
| Description: |
The call vsf_udpat sets up a new fill-pattern, freely defined
by the user. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| pfill_pat |
Pointer to an array of 16 * planes WORDs that define
the bit pattern for a line of the fill
|
| planes |
Number of colour planes
|
Notes: Each line reproduces the fill-pattern for one
colour plane. The first entry of a line corresponds here to the first
line of the pattern, etc.
Patterns with multiple colours have to be stored in standard
format and must have the same number of planes as the device.
Exception: If the device is a HiColor or TrueColor device (direct
colour mapping) you always pass a pattern width of 32-bit pixels
(xrgb) and pfill_pat points to a 16 * 16 array of LONGs.
If you use a pattern with multiple colours you should select
colour index 1 and writing mode REPLACE.
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Fill attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vsf_interior
|
| C: |
void vsf_udpat ( int16_t handle, int16_t *pfill_pat, int16_t
planes );
|
| Binding: |
void vsf_udpat (int16_t handle, int16_t *pfill_pat,
int16_t planes)
{
intin[0..16n-1] = pfill_pat[0..16n-1];
contrl[0] = 112;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = planes * 16;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set fill perimeter visibility« - Determine whether an
outline is to be drawn round filled areas.
|
| Opcode: |
104
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsf_xperimeter ( int16_t handle, int16_t on_off,
int16_t f_or_l );
|
| Description: |
This function turns the outline border of a filled area
(rectangle, polygon, ellipse, ...) on or off and sets the line style
for the perimeter outline.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| on_off |
Desired mode:
| 0 = |
Turn perimeter outlining off
|
| 1 = |
Turn perimeter outlining on
|
| -1 = |
Do not change perimeter outlining
|
|
| f_or_l |
Line type, as for vsl_type:
| 0 = |
Use normal fill colour for perimeter
|
| 1 = |
Use line style attributes for perimeter
|
|
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the mode actually set.
|
| Availability: |
GEM/3 Release 3.1
|
| Group: |
Fill attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vsf_perimeter v_fillarea v_contourfill vr_recfl
v_bar v_pieslice v_circle v_ellipse v_ellpie v_rfbox
|
| Name: |
»Set background colour« - Set background colour for lines.
|
| Opcode: |
201 (Sub-Opcode 2)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsl_bg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
The call vsl_bg_color sets the background colour for drawn
lines.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY of the background colour
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
NVDI 5.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Lines attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set polyline colour index« - Set the line colour.
|
| Opcode: |
17
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsl_color ( int16_t handle, int16_t color_index );
|
| Description: |
The call vsl_color sets the colour index for lines.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_index |
Line colour
|
Note: The colour indices 0 and 1 are available on all
devices; all other values depend on the output device being used at
the time.
If the index is invalid, colour index 1 will be selected.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the line colour actually set.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all devices.
|
| Group: |
Lines attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_pline v_arc v_ellarc v_rbox
|
| Name: |
»Set polyline end styles« - Set the shape of line ends.
|
| Opcode: |
108
|
| Syntax: |
void vsl_ends ( int16_t handle, int16_t beg_style, int16_t
end_style );
|
| Description: |
The call vsl_ends sets the appearance of the line ends. The
following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning Symbole
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| beg_style |
End style for the first point:

| 0 = |
Squared (default)
|
| 1 = |
Arrowed
|
| 2 = |
Rounded
|
|
| end_style |
End style for the last point (as above)
|
Note: Both the squared style and the arrow style end at
the end of the polyline. The rounded style is drawn such that the
center of the rounding is at the end of the polyline.
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all devices.
|
| Group: |
Lines attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_pline v_arc v_ellarc v_rbox
|
| C: |
void vsl_ends ( int16_t handle, int16_t beg_style, int16_t
end_style );
|
| Binding: |
void vsl_ends (int16_t handle, int16_t beg_style,
int16_t end_style)
{
intin[0] = beg_style;
intin[1] = end_style;
contrl[0] = 108;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 2;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set foreground colour« - Set foreground colour for lines.
|
| Opcode: |
200 (Sub-Opcode 2)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsl_fg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
The call vsl_fg_color sets the foreground colour for drawn
lines.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY of the foreground colour
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
NVDI 5.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Lines attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set polyline type« - Set the line type.
|
| Opcode: |
15
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsl_type ( int16_t handle, int16_t style );
|
| Description: |
The call vsl_type sets the line type for polyline operations.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| style |
Requested line type:
| 1 = |
Solid
|
| 2 = |
Long dash
|
| 3 = |
Dot
|
| 4 = |
Dash,dot
|
| 5 = |
Dash
|
| 6 = |
Dash,dot,dot
|
| 7 = |
User-defined, vsl_udsty
|
|
Note: Line types from the value 8 on depend on the
output device in each case. If the requested line type is not
available, line type 1 will be selected (solid).
You can obtain the available line types with the function
vq_extnd.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the line type actually set.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all devices.
|
| Group: |
Lines attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_pline v_arc v_ellarc v_rbox vsl_udsty
|
| Name: |
»Set user-defined line style pattern«
|
| Opcode: |
113
|
| Syntax: |
void vsl_udsty ( int16_t handle, int16_t pattern );
|
| Description: |
The call vsl_udsty sets the freely-definable line style for
vsl_type. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| pattern |
Line style pattern WORD, 16 bits
|
Note: The Most Significant Bit (MSB) of the
pattern WORD is the first pixel in the line. The default value
is a completely solid line.
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all devices.
|
| Group: |
Lines attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vsl_type
|
| Name: |
»Set polyline width«
|
| Opcode: |
16
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsl_width ( int16_t handle, int16_t width );
|
| Description: |
The call vsl_width sets the line width for lines and
perimeters. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| width |
Line width (must be odd!)
|
Note: The width of the line always refers to the
coordinates in the X-direction. As the VDI can only draw lines an
odd number of pixels thick, the actually set width is smaller or equal
to the selected width as values will be rounded down to the nearest
odd number. The function is not available on all output
devices.
Most device drivers ignore the line type and draw solid lines if
the line is more than one pixel wide.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the line width actually set.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all devices.
|
| Group: |
Lines attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_pline v_arc v_ellarc v_rbox
|
| Name: |
»Set Bezier quality« - Set quality of the Bezier spline
creation.
|
| Opcode: |
5 (Escape 99, Opcode 32)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t v_bez_qual ( int16_t handle, int16_t qual, int16_t
*set_qual );
|
| Description: |
The call v_bez_qual sets a new factor that determines the
quality and speed with which Bezier splines are drawn. The following
apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| qual |
Requested Bezier quality
|
| set_qual |
Realized Bezier quality (not available with GEM/3 Release
3.1).
|
Note: The quality of the Beziers can be set as usual in
percent (i.e. from 0 to 100), where 0 is fastest but produces the
lowest quality while 100 is slowest with the highest possible quality.
set_qual may not be an exact percentage as the rendering
engine may not support every possible value between 1 and 99.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the quality factor actually set.
The GEM/3 and NVDI bindings also returns set_qual.
|
| Availability: |
As of GEM/3 Release 3.1, SpeedoGDOS 4.00 onwards and NVDI
2.10 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Lines attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_bez_on v_bez_off v_bez v_bez_fill
v_set_app_buff
|
| Name: |
»Set background colour« - Set background colour for markers.
|
| Opcode: |
201 (Sub-Opcode 3)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsm_bg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
The call vsm_bg_color sets the background colour for markers.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY of the background colour
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
NVDI 5.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Marker attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set polymarker colour index« - Set the colour of the marker
points.
|
| Opcode: |
20
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsm_color ( int16_t handle, int16_t color_index );
|
| Description: |
The call vsm_color sets the colour of the markers. The
following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_index |
Marker colour
|
Note: The colour indices 0 and 1 are always available,
all further ones depend on the output device. If the index is invalid,
colour index 1 will be selected.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the colour index actually selected.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all devices.
|
| Group: |
Marker attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_pmarker
|
| Name: |
»Set foreground colour« - Set foreground colour for markers.
|
| Opcode: |
200 (Sub-Opcode 3)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsm_fg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
The call vsm_fg_color sets the foreground colour for markers.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY of the foreground colour
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
NVDI 5.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Marker attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set polymarker height« - Set height of the marker object.
|
| Opcode: |
19
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsm_height ( int16_t handle, int16_t height );
|
| Description: |
The call vsm_height sets the current marker height.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| height |
Requested polymarker height (pixels)
|
The number of available heights can be obtained during opening
of the virtual workstation with v_opnvwk.
Note: The width of the markers is adapted automatically.
If an invalid height is chosen, the VDI selects the next suitable
one. The dot's size can not be altered, it is always one pixel
high and wide.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the size actually selected.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all devices.
|
| Group: |
Marker attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_pmarker
|
| C: |
int16_t vsm_height ( int16_t handle, int16_t height );
|
| Binding: |
int16_t vsm_height (int16_t handle, int16_t height)
{
ptsin[0] = 0;
ptsin[1] = height;
contrl[0] = 19;
contrl[1] = 1;
contrl[3] = 0;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
return ( ptsout[1] );
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
Note: The component set_height_x describes the
selected marker height with reference to the X-direction; PC-GEM
always returns the value 0.
|
| Name: |
»Set polymarker type« - Set the type of the marker object.
|
| Opcode: |
18
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vsm_type ( int16_t handle, int16_t typ );
|
| Description: |
The call vsm_type determines the appearance of the current
marker. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning Symbole
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| typ |
Polymarker type:
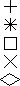
| 1 = |
Dot
|
| 2 = |
Plus
|
| 3 = |
Asterisk
|
| 4 = |
Square
|
| 5 = |
Diagonal cross
|
| 6 = |
Diamond
|
| 7 ... n = |
Device-dependent
|
|
Note: If the requested marker type is out of range, the
GEM VDI will use an asterisk, type 3. Marker 1 is the smallest dot that
GEM VDI can depict on the device (usually one pixel); it cannot be
scaled.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the marker actually selected.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all devices.
|
| Group: |
Marker attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_pmarker vsm_height
|
| Name: |
»Set graphic text alignment« - Set the alignment for normal
and justified text output.
|
| Opcode: |
39
|
| Syntax: |
void vst_alignment ( int16_t handle, int16_t hor_in, int16_t
vert_in, int16_t *hor_out, int16_t *vert_out );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_alignment determines the horizontal and vertical
alignment of a text.
Example:
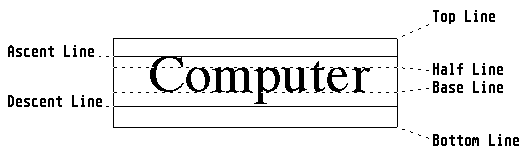
The function is passed the following Parameters:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| hor_in |
Horizontal alignment:
| 0 = |
Left justified (default)
|
| 1 = |
Centered
|
| 2 = |
Right justified
|
|
| vert_in |
Vertical alignment:
| 0 = |
Baseline (default)
|
| 1 = |
Half line
|
| 2 = |
Ascent line
|
| 3 = |
Bottom line
|
| 4 = |
Descent line
|
| 5 = |
Top line
|
|
| hor_out |
Selected horizontal alignment
|
| vert_out |
Selected vertical alignment
|
Note: The default setting is the left edge of the
baseline. For an invalid input for the horizontal alignment, the text
is flushed left ('left-justified'). For an invalid input for the
vertical alignment, the text will be aligned on the baseline.
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_gtext v_justified
|
| C: |
void vst_alignment ( int16_t handle, int16_t hor_in, int16_t
vert_in, int16_t *hor_out, int16_t *vert_out );
|
| Binding: |
void vst_alignment (int16_t handle, int16_t hor_in,
int16_t vert_in, int16_t *hor_out,
int16_t *vert_out)
{
intin[0] = hor_in;
intin[1] = vert_in;
contrl[0] = 39;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 2;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*hor_out = intout[0];
*vert_out = intout[1];
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set character cell height in arbitrary points« - Set the
character cell height in points.
|
| Opcode: |
246
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_arbpt ( int16_t handle, int16_t point, int16_t
*chwd, int16_t *chht, int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_arbpt sets the current character height for an
outline font in printer points. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| point |
Desired character height
|
| chwd |
Resulting character width
|
| chht |
Resulting character height
|
| cellwd |
Resulting character cell width
|
| cellht |
Resulting character cell height
|
Notes: In contrast to vst_point, the function permits
the scaling to any integer point size, irrespective of the
sizes listed in EXTEND.SYS. If you want to set a fractional point
size, use vst_arbpt32.
If negative values are set, the characters will be mirrored
(reflected) about the X-axis.
The returned character widths are rounded-off values, which
cannot be used without more ado for calculating overall text widths.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the character height set in points.
|
| Availability: |
With FSM-GDOS, and SpeedoGDOS Version 4.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vst_arbpt32 vst_point vst_setsize SpeedoGDOS
NVDI
|
| C: |
int16_t vst_arbpt ( int16_t handle, int16_t point, int16_t
*chwd, int16_t *chht, int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht );
|
| Binding: |
int16_t vst_arbpt (int16_t handle, int16_t point,
int16_t *chwd, int16_t *chht,
int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht)
{
intin[0] = point;
contrl[0] = 246;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 1;
contrl[5] = 0;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*chwd = ptsout[0];
*chht = ptsout[1];
*cellwd = ptsout[2];
*cellht = ptsout[3];
return ( intout[0] );
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set character cell height in arbitrary points« - Set the
character cell height in points for an outline font.
|
| Opcode: |
246
|
| Syntax: |
fix31 vst_arbpt32 ( int16_t handle, fix31 point, int16_t *chwd,
int16_t *chht, int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_arbpt32 sets the current character height for an
outline font in printer points, and can include fractional sizes. The
following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| point |
Desired character height
|
| chwd |
Resulting character width
|
| chht |
Resulting character height
|
| cellwd |
Resulting character cell width
|
| cellht |
Resulting character cell height
|
Notes: In contrast to vst_point, the function permitsthe
scaling to any point size, irrespective of the values listed
in EXTEND.SYS.
If negative values are set, the characters will be mirrorred
(reflected) about the X-axis.
The returned character widths are rounded-off values, which
cannot be used without more ado for calculating overall text widths.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the character height actually set in
1/65536 of a point.
This is not clear from the SpeedoGDOS documentation. It's
possible that only the character height in points is returned.
|
| Availability: |
With FSM-GDOS, SpeedoGDOS as of Version 4.00, and NVDI 3.00
onwards. In the documentation for NVDI 3.00 this function is wrongly
called vst_arbpt.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vst_point vst_setsize SpeedoGDOS NVDI
|
| C: |
fix31 vst_arbpt32 ( int16_t handle, fix31 point, int16_t *chwd,
int16_t *chht, int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht );
|
| Binding: |
fix31 vst_arbpt32 (int16_t handle, fix31 point,
int16_t *chwd, int16_t *chht,
int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht)
{
intin[0..1] = point;
contrl[0] = 246;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 2;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*chwd = ptsout[0];
*chht = ptsout[1];
*cellwd = ptsout[2];
*cellht = ptsout[3];
return ( intout[0..1] );
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set background color« - Set background colour for text.
|
| Opcode: |
201 (Sub-Opcode 0)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_bg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_bg_color sets the background colour for text.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY of the background colour
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
NVDI 5.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set character mapping mode« - Select the type of font
indexing.
|
| Opcode: |
236
|
| Syntax: |
void vst_charmap ( int16_t handle, int16_t mode );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_charmap sets the type of font indexing, offering a
choice between the standard Atari ASCII interpretation of text strings
or the Bitstream character indices. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| mode |
Mapping mode:
| 0 = |
Direct mapping (WORD), i.e. no translation of the character
index
|
| 1 = |
ASCII mapping (byte-sized)
|
|
For SpeedoGDOS the following applies:
| mode |
Type of indexing:
| 0 = |
Atari characters
|
| 1 = |
Bitstream
|
|
Note: If you switch to direct mapping, the number of
characters per font (minADE and maxADE/vqt_fontinfo)
is changed to the number of really existing characters.
As of NVDI 4.00 there is an extended version: vst_map_mode
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
SpeedoGDOS 4.0, NVDI 3.00
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vst_map_mode vqt_fontinfo ASCII table
|
| Name: |
»Set graphic text colour index« - Set the colour of the text
output.
|
| Opcode: |
22
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_color ( int16_t handle, int16_t color_index );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_color sets the colour index for subsequent graphic
text operations.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_index |
Requested text colour index
|
Note: All devices support at least two colour indices, 0
and 1 (monochrome). All others depend on the output device in use. If
an invalid index is specified then the value 1 will be assumed.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the colour actually set.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_gtext v_justified
|
| Name: |
»Set graphic text special effects«
|
| Opcode: |
106
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_effects ( int16_t handle, int16_t effect );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_effects defines various special effects to be
applied to text. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| effect |
Texteffekt in Bit-Darstellung
| 0x00 = |
Normal
|
| 0x01 = |
Thickened
|
| 0x02 = |
Lightened
|
| 0x04 = |
Skewed
|
| 0x08 = |
Underlined
|
| 0x10 = |
Outlined
|
| 0x20 = |
Shadowed (not currently supported)
|
|
Notes: The text effects can also be mixed with an OR
combination; unavailable effects will not be set.
Apart from underlining, these special effects do not usually
work well with outline (vector) text.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the text effect actually selected.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_gtext v_justified
|
| Name: |
»Set outline font error mode« - Set the GDOS error
handling.
|
| Opcode: |
245
|
| Syntax: |
void vst_error ( int16_t handle, int16_t mode, int16_t
*errorvar );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_error determines the type of GDOS error handling
and can stop error-messages being sent to the screen. The following
apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| mode |
Type of error handling:
| 0 = |
Errors reported in error variable errorvar
|
| 1 = |
Default) Errors go to screen
|
|
| errorvar |
Address of the error variables; should be initialized with a
NULL. The following error codes apply for SpeedoGDOS 4.xx:
| 1 = |
Out of system memory (Misc cache)
|
| 2 = |
Error opening font file
|
| 3 = |
Error reading font file
|
| 4 = |
Error while writing out cache buffer
|
| 5 = |
Font scaler error
|
| 6 = |
(Not implemented)
|
| 7 = |
Not enough memory for scratch buffer
|
| 8 = |
Out of system memory (character cache)
|
| 255 = |
Misc. Speedo error
|
With SpeedoGDOS 5.0 the meaning seems to have altered to:
| 1 = |
Insufficient font data loaded
|
| 3 = |
Invalid font specifications ordered
|
| 4 = |
Font format error (very often a customer-specific font that is
licensed only for a given program).
|
| 5 = |
Requested specs not compatible with output module
|
| 7 = |
Rules requested; not supported
|
| 8 = |
Mode not available
|
| 10 = |
Font not specified
|
| 11 = |
Squeezing/Clipping requested but not supported
|
| 12 = |
Character data not available
|
| 13 = |
Track kerning data not available
|
| 14 = |
Pair kerning data not available
|
NVDI >= 3.01 will report the error codes from SpeedoGDOS 5.0
when dealing with Speedo fonts. Additionally, it will report several
error codes >= 0x1000 when dealing with TrueType fonts:
| 0x1000 = |
Out of system memory (Misc cache)
|
|
Notes: The error variable errorvar should be
checked before the call of the following GDOS functions:
v_gtext v_ftext
v_justified vst_point
vst_height vst_font
vst_arbpt vqt_advance
vst_setsize vqt_fontinfo
vqt_name vqt_width
vqt_extent vqt_f_extent
v_opnwk v_opnvwk
vst_load_fonts vst_unload_fonts
It is up to each application to process the errors correctly. It
should also reset the value pointed to by errorvar to 0 after
each reported error.
|
| Return value: |
This function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
With FSM-GDOS, Font-GDOS, SpeedoGDOS as of Version 4.00, and
NVDI as of version 3.01.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding GDOS SpeedoGDOS
|
| Name: |
»Set foreground colour« - Set foreground colour for text.
|
| Opcode: |
200 (Sub-Opcode 0)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_fg_color ( int16_t handle, int32_t color_space,
COLOR_ENTRY *fg_color );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_fg_color sets the foreground colour for text.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color_space |
Colour space (at present only 0 for the colour space set, or
CSPACE_RGB)
|
| fg_color |
COLOR_ENTRY of the foreground colour
|
|
| Return value: |
-1 = Wrong subfunction number
0 = Function not present
1 = All OK
|
| Availability: |
NVDI 5.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set text face« - Select a font for text output.
|
| Opcode: |
21
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_font ( int16_t handle, int16_t font );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_font selects the current font for outputting text.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| font |
Requested font
|
Note: The names and indices of the fonts can be obtained
with the function vqt_name. Whether the fonts are supported depends on
the output device in each case.
If a requested font does not exist, the system font will be
chosen.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the number of the selected font.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vst_load_fonts vqt_name v_gtext v_justified
|
| Name: |
»Set character height, absolute mode« - Set the character
height for text output.
|
| Opcode: |
12
|
| Syntax: |
void vst_height ( int16_t handle, int16_t height, int16_t
*char_width, int16_t *char_height, int16_t *cell_width, int16_t
*cell_height );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_height sets the character height in pixels.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| height |
Requested character height
|
| char_width |
Selected character width
|
| char_height |
Selected character height
|
| cell_width |
Selected character cell width
|
| cell_height |
Selected character cell height
|
Note: If the desired character height does not map
exactly to a device size, VDI selects the closest character size
that does not exceed the requested size.
Most screen drivers using this function can reduce available
fonts by any amount, or scale them to double size. This applies in
particular to the screen driver implemented in ROM.
If the font is a vector font, char_width and
cell_width are not the exact character widths but only rounded
values.
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_gtext v_justified vst_point
|
| C: |
void vst_height ( int16_t handle, int16_t height, int16_t
*char_width, int16_t *char_height, int16_t *cell_width, int16_t
*cell_height );
|
| Binding: |
void vst_height (int16_t handle, int16_t height,
int16_t *char_width, int16_t *char_height,
int16_t *cell_width, int16_t *cell_height)
{
ptsin[0] = 0;
ptsin[1] = height;
contrl[0] = 12;
contrl[1] = 1;
contrl[3] = 0;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*char_width = ptsout[0];
*char_height = ptsout[1];
*cell_width = ptsout[2];
*cell_height = ptsout[3];
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set kerning mode«
|
| Opcode: |
237
|
| Syntax: |
void vst_kern ( int16_t handle, int16_t tmode, int16_t pmode,
int16_t *tracks, int16_t *pairs );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_kern permits setting of the desired kerning mode
and its values.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| tmode |
Track kerning:
| 0 = |
No track kerning
|
| 1 = |
Normal
|
| 2 = |
Tight
|
| 3 = |
Very tight
|
|
| pmode |
Pair kerning:
| 0 = |
No pair kerning
|
| 1 = |
Use pair kerning
|
|
| tracks |
Track kerning mode
|
| pairs |
Number of kerning pairs defined in font
|
Note: Most Speedo fonts have 3 kerning tracks. Ordinary
TrueType fonts do not have any kerning tracks, but some GX TrueTypes
do.
NVDI allows the caller to set a user-defined track kerning
(vst_track_offset). The track kerning mode must be 255 (track_mode)
and intin[2..3] contain the offset in 1/65536 pixels.
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
As of SpeedoGDOS 4.00, and NVDI 3.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vqt_pairkern vqt_trackkern vst_track_offset
|
| C: |
void vst_kern ( int16_t handle, int16_t tmode, int16_t pmode,
int16_t *tracks, int16_t *pairs );
|
| Binding: |
void vst_kern (int16_t handle, int16_t tmode, int16_t pmode,
int16_t *tracks, int16_t *pairs)
{
intin[0] = tmode;
intin[1] = pmode;
contrl[0] = 237;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 2;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*tracks = intout[0];
*pairs = intout[1];
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set character mapping mode« - Set the type of font indexing
(extended version of vst_charmap).
|
| Opcode: |
236
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_map_mode ( int16_t handle, int16_t mode );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_map_mode sets the type of font indexing, allowing
choices between standard Atari ASCII interpretation of text strings,
the Bitstream character indices or Unicode mapping. The following
apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| mode |
Mapping mode:
| 0 = |
Direct mapping (WORD), i.e. no translation of the character
index
|
| 1 = |
ASCII mapping (byte-sized)
|
| 2 = |
Unicode mapping (WORD)
|
|
Note: If you switch to direct mapping, the number of
characters per font (minADE and maxADE/vqt_fontinfo)
is changed to the number of really existing characters.
If you select Unicode and if you want to determine whether a
certain character exists, you should call vqt_width. If the index
returned by vqt_width is -1, the character does not exist. Instead of
vqt_width you can also call vqt_char_index and map the Unicode index
into a direct index.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the selected mapping.
|
| Availability: |
NVDI 4.0
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vst_charmap vqt_fontinfo ASCII table
|
| Name: |
»Set text face by name« - Find and set font.
|
| Opcode: |
230 (Opcode 0)
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_name ( int16_t handle, int16_t font_format, int8_t
*font_name, int8_t *ret_name );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_name searches for a font by name, and sets it as
the current one.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| font_format |
Possible font formats:
| 1 = |
Bitmap font
|
| 2 = |
Speedo font
|
| 4 = |
TrueType font
|
| 8 = |
Type-1 font
|
|
| font_name |
Font name
|
| ret_name |
Name of the selected font
|
Note: Missing or extra spaces in the font name are
ignored. If the requested font is not available, the system font is
selected.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the ID of the selected font.
|
| Availability: |
The function is available under NVDI as of Version 3.02.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vqt_name vqt_xfntinfo
|
| C: |
int16_t vst_name ( int16_t handle, int16_t font_format, int8_t
*font_name, int8_t *ret_name );
|
| Binding: |
int16_t vst_name (int16_t handle, int16_t font_format,
int8_t *font_name, int8_t *ret_name)
{
intin[0] = font_format;
intin[1..n] = font_name[0..n-1];
contrl[0] = 230;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = n;
contrl[5] = 0;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
ret_name[0..m-1] = intout[1..m];
return ( intout[0] );
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set character height, points mode« - Set the character cell
size for text output.
|
| Opcode: |
107
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_point ( int16_t handle, int16_t point, int16_t
*char_width, int16_t *char_height, int16_t *cell_width, int16_t
*cell_height );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_point sets the character cell size, i.e. the
distance between two baselines, in points (1/72"). The following
apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| point |
Requested character cell height (points)
|
| char_width |
Selected character width
|
| char_height |
Selected character height
|
| cell_width |
Selected character cell width
|
| cell_height |
Selected character cell height
|
The sizes are measured in points, each of which is 1/72 inch or
roughly 0.353mm.
Note: Should the desired character height not be
available, the next smaller one will be chosen. With proportional
fonts, the maximum possible values are returned for width and height.
If the font is a vector font, only predefined heights can be
selected (usually 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 18, 24, 36, and 48 pt).
Warning: The screen driver in ROM can scale each of the
available fonts to double size, so that it is not possible
without further ado to differentiate between fonts that have been
scaled and those actually present. One can help oneself here by using
a routine that can locate all present point sizes, as, when a
wrong size is specified, vst_point selects the next smallest available
size; if one finds with this method that all point sizes are
present, then we are evidently dealing with a vector font.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the character cell height in points.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_gtext v_justified vst_height
|
| C: |
int16_t vst_point ( int16_t handle, int16_t point, int16_t
*char_width, int16_t *char_height, int16_t *cell_width, int16_t
*cell_height );
|
| Binding: |
int16_t vst_point (int16_t handle, int16_t point,
int16_t *char_width, int16_t *char_height,
int16_t *cell_width, int16_t *cell_height)
{
intin[0] = point;
contrl[0] = 107;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 1;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*char_width = ptsout[0];
*char_height = ptsout[1];
*cell_width = ptsout[2];
*cell_height = ptsout[3];
return ( intout[0] );
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set character baseline vector« - Set the orientation of the
baseline for text output.
|
| Opcode: |
13
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_rotation ( int16_t handle, int16_t angle );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_rotation sets the orientation of the baseline for
graphic text output. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| angle |
Requested angle of rotation of character baseline
|
Note: The angle is specified in 1/10 of a degree. If the
selected font is a bitmap font, rotation works only in steps of 90
degrees; for vector fonts it is continuous. On some devices this
function is not available.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the angle actually selected.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all drivers. For specific character rotation
abilities, check the values returned in vq_extnd.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_gtext v_justified
|
| Name: |
»Set scratch buffer allocation mode«
|
| Opcode: |
244
|
| Syntax: |
void vst_scratch ( int16_t handle, int16_t mode );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_scratch selects the way that the scratch buffer is
created. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| mode |
Type of buffer
| 0 = |
Allocated size is large enough for bitmap and vector fonts with
any special text effects (default)
|
| 1 = |
Size is governed by the bitmap fonts; one should forgo text
effects for vector fonts
|
| 2 = |
Do not create a scratch buffer, and forgo text effects
|
|
Notes: The scratch buffer is used for generation of text
effects. As vector fonts are freely scalable, one cannot allocate a
unique size for the scratch buffer.
Atari recommends that at least mode 1 is set prior to
vst_load_fonts to prevent scratch buffer overruns.
|
| Return value: |
This function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
FSM-GDOS, and SpeedoGDOS as of version 4.00.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding GDOS SpeedoGDOS vst_effects
|
| Name: |
»Set character cell width in points« - Set the character cell
width in points.
|
| Opcode: |
252
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_setsize ( int16_t handle, int16_t point, int16_t
*chwd, int16_t *chht, int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_setsize sets the character width in points
(1/72") for outline characters. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| point |
Desired character width in points
|
| chwd |
Resultant character width
|
| chht |
Resultant character height
|
| cellwd |
Resultant character cell width
|
| cellht |
Resultant character cell height
|
Note: The next call of vst_point, vst_arbpt or
vst_height resets the width set by this function and the width
required by the relevant characters is set instead. With negative
widths the characters will be mirrored about the Y-axis.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the character cell width set in points.
|
| Availability: |
FSM-GDOS, and SpeedoGDOS as of version 4.00.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vst_setsize32 vst_point vst_height vst_arbpt
|
| C: |
int16_t vst_setsize ( int16_t handle, int16_t point, int16_t
*chwd, int16_t *chht, int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht );
|
| Binding: |
int16_t vst_setsize (int16_t handle, int16_t point,
int16_t *chwd, int16_t *chht,
int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht)
{
intin[0] = point;
contrl[0] = 252;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 1;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*chwd = ptsout[0];
*chht = ptsout[1];
*cellwd = ptsout[2];
*cellht = ptsout[3];
return ( intout[0] );
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set character cell width in arbitrary points« - Set the
character cell width in fractional points.
|
| Opcode: |
252
|
| Syntax: |
fix31 vst_setsize32 ( int16_t handle, fix31 point, int16_t
*chwd, int16_t *chht, int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_setsize32 sets the character width as a fix31
fractional value in 1/65536 of a point.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| point |
Desired character width (in points)
|
| chwd |
Selected character width
|
| chht |
Selected character height
|
| cellwd |
Selected character cell width
|
| cellht |
Selected character cell height
|
Note: A call of vst_point, vst_arbpt or vst_height
resets the width set by this function and the width required by the
relevant characters is set instead. With negative widths the
characters are mirrored about the Y-axis.
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the set character cell width in 1/65536 of
a point.
|
| Availability: |
As of SpeedoGDOS 4.00, and NVDI 3.00 onwards. In the
documentation for NVDI 3.00 this function is wrongly called
vst_setsize.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vst_point vst_height vst_arbpt
|
| C: |
fix31 vst_setsize32 ( int16_t handle, fix31 point, int16_t
*chwd, int16_t *chht, int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht );
|
| Binding: |
fix31 vst_setsize32 (int16_t handle, fix31 point,
int16_t *chwd, int16_t *chht,
int16_t *cellwd, int16_t *cellht)
{
intin[0..1] = point;
contrl[0] = 252;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 2;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*chwd = ptsout[0];
*chht = ptsout[1];
*cellwd = ptsout[2];
*cellht = ptsout[3];
return ( intout[0..1] );
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set outline font skew« - Set the slope for 'italic' text.
|
| Opcode: |
253
|
| Syntax: |
int16_t vst_skew ( int16_t handle, int16_t skew );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_skew sets the skew of vector font characters in
steps of 1/10 degrees. The skewing angle is independent of vst_effects
and must be in a range between -90 and +90 degrees. Positive angles
will lean the characters to the left, whereas negative angles will
lean them to the right.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| skew |
Angle in 1/10 degrees
|
Note: This function can really only be seen as a bit of
a lark, as characters created in this way basically look worse than a
true italic font (which should be available for most font families).
|
| Return value: |
The function returns the set skew angle.
|
| Availability: |
FSM-GDOS, SpeedoGDOS as of Version 4.00, and NVDI 3.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vst_effects SpeedoGDOS NVDI
|
| Name: |
Set track kerning offset« - Set offset for track kerning.
|
| Opcode: |
237 (Opcode 255)
|
| Syntax: |
void vst_track_offset ( int16_t handle, fix31 offset, int16_t
pairmode, int16_t *tracks, int16_t *pairs );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_track_offset allows the setting of a user-defined
value for track kerning. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| offset |
Offset
|
| pairmode |
Pair kerning:
|
| tracks |
Track kerning mode
|
| pairs |
Number of kerning pairs
|
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
NVDI 3.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vqt_pairkern vqt_trackkern vst_kern
|
| Name: |
»Set character width (absolute mode)« - Set character width
in pixels.
|
| Opcode: |
231
|
| Syntax: |
void vst_width ( int16_t handle, int16_t width, int16_t
*char_width, int16_t *char_height, int16_t *cell_width, int16_t
*cell_height );
|
| Description: |
The call vst_width sets the character width in pixels. The
following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| width |
Desired character width
|
| char_width |
Selected character width
|
| char_height |
Seleted character height
|
| cell_width |
Selected character cell width
|
| cell_height |
Selected character cell height
|
Note: The next call of vst_height, vst_point or
vst_arbpt32 resets the width. You should use vst_setsize32 instead of
vst_width because vst_width uses only an integer value as a relative
width and therefore it does not offer the required accuracy.
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
As of SpeedoGDOS 4.20, and NVDI 3.00 onwards.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding vst_arbpt vst_height vst_point vst_setsize
|
| C: |
void vst_width ( int16_t handle, int16_t width, int16_t
*char_width, int16_t *char_height, int16_t *cell_width, int16_t
*cell_height );
|
| Binding: |
void vst_width (int16_t handle, int16_t width,
int16_t *char_width, int16_t *char_height,
int16_t *cell_width, int16_t *cell_height)
{
ptsin[0] = width;
contrl[0] = 231;
contrl[1] = 1;
contrl[3] = 0;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*char_width = ptsout[0];
*char_height = ptsout[1];
*cell_width = ptsout[2];
*cell_height = ptsout[3];
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set character height, absolute mode« - Set character height
for text output.
|
| Opcode: |
5 (Escape 18501)
|
| Syntax: |
void v_topbot ( int16_t handle, int16_t height, int16_t
*char_width, int16_t *char_height, int16_t *cell_width, int16_t
*cell_height );
|
| Description: |
The call v_topbot is an alternative to vst_height. It uses top
to bottom distance for text scaling, instead of top to baseline
distance.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| height |
Character height
|
| char_width |
Selected character width
|
| char_height |
Selected character height
|
| cell_width |
Character cell width
|
| cell_height |
Character cell height
|
Note: If the desired character height is not available,
the next smaller one is chosen automatically. With proportional fonts,
the output parameters contain the width of the widest character in the
font.
Most screen drivers using this function can reduce available
fonts by any amount, or scale them to double size. This applies in
particular to the screen driver implemented in ROM.
With vector fonts, the widths output by char_width and
cell_width represent rounded-off values.
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
GEM/3 Release 3.1.
|
| Group: |
Text attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_gtext v_justified vst_point vst_height
|
| C: |
void v_topbot ( int16_t handle, int16_t height, int16_t
*char_width, int16_t *char_height, int16_t *cell_width, int16_t
*cell_height );
|
| Binding: |
void v_topbot (int16_t handle, int16_t height,
int16_t *char_width, int16_t *char_height,
int16_t *cell_width, int16_t *cell_height)
{
ptsin[0] = 0;
ptsin[1] = height;
contrl[0] = 5;
contrl[1] = 1;
contrl[3] = 0;
contrl[5] = 18501;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
*char_width = ptsout[0];
*char_height = ptsout[1];
*cell_width = ptsout[2];
*cell_height = ptsout[3];
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set background colour«
|
| Opcode: |
5 (Escape 102)
|
| Syntax: |
void vs_bkcolor ( int16_t handle, int16_t color );
|
| Description: |
The call vs_bkcolor sets the background colour for the device
associated with handle, usually a camera device.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| color |
Background colour index
|
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
GEM/3 Release 3.1
|
| Group: |
Superior attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set colour representation« - Set the colour intensity of a
palette index.
|
| Opcode: |
14
|
| Syntax: |
void vs_color ( int16_t handle, int16_t index, int16_t *rgb_in
);
|
| Description: |
The call vs_color sets the colour intensity for the individual
colour registers of a palette index. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| index |
Colour register index (pen)
|
| rgb_in[0] |
Red colour intensity (in tenths of a percent, 0-1000)
|
| rgb_in[1] |
Green colour intensity (in tenths of a percent, 0-1000)
|
| rgb_in[2] |
Blue colour intensity (in tenths of a percent, 0-1000)
|
As not every output device needs to offer 1000 possible colour
tints, several input intensities of the RGB colours may share the
intensities that have actually been set.
Note: The function can only be used if lookup table support is
present. If an invalid colour number is passed, then the next
achievable value will be set.
For devices with a CLUT (graphics systems with up to 8 planes,
i.e. 256 colours) the settings are effective immediately on all pixels
that were drawn on the screen with the colour index index.
Important: For this reason the first 16 colour numbers
should not be altered, as these are used by the AES.
If a device has more than 256 colours displayable
simultaneously, it usually does not have a CLUT. In that case the
pixels do not contain a colour value or index but a direct colour
value in RGB (e.g. a pixel with 32 bits has 8 unused bits, 8 bits for
red, 8 bits for green and 8 bits for blue). This means that the VDI
creates a pseudo-CLUT with 256 pens, and calling vs_color for one of
these pens will not change the colour of the pixels which have been
drawn with this pen, though it will change the colour of new pixels
drawn with this pen. Note that the palettes are handled per
workstation, which means that each workstation has its own palette
(pseudo-CLUT) and changing the RGB value for a colour index on one
workstation will not change the value of the same pen on another
workstation.
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
Supported by all devices.
|
| Group: |
Superior attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_pline v_pmarker v_gtext v_fillarea
v_cellarray v_contourfill vr_recfl v_bar v_arc v_pieslice
v_circle v_ellarc v_ellpie v_ellipse v_rbox v_rfbox
v_justified vq_color vq_scrninfo
|
| C: |
void vs_color ( int16_t handle, int16_t index, int16_t *rgb_in
);
|
| Binding: |
void vs_color (int16_t handle, int16_t index, int16_t *rgb_in)
{
int16_t i;
intin[0] = index;
for (i=1; i<4; i++)
intin[i] = *rgb_in++;
contrl[0] = 14;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 4;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|
| Name: |
»Set colour representation-2« - Set colour intensity and
colour for attributes.
|
| Opcode: |
138 (Opcode 0,1,2)
|
| Syntax: |
void vs_color2 ( int16_t handle, int16_t *rgb, int16_t index );
|
| Description: |
The call vs_color2 sets the colour intensity and colour for
certain attribute functions. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| rgb[0] |
Red portion in tenths of a percent
|
| rgb[1] |
Green portion in tenths of a percent
|
| rgb[2] |
Blue portion in tenths of a percent
|
| index |
Colour number
|
Note: The function is available directly only
under PC-GEM. However it can be emulated on the Atari, which some
applications (e.g. Kandinsky and GEM) actually do.
It works similarly to vs_color, with the difference that with an
opcode of
| 0 |
the text colour
|
| 1 |
the fill colour
|
| 2 |
the line colour
|
is altered, and so the corresponding calls of vsl_color etc. are
no longer necessary. Due to lack of documentation, one unfortunately
cannot say for certain whether the name of the function
(vs_color2) is really correct.
|
| Return value: |
Die Funktion liefert kein Ergebnis zurück.The function does
not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
The above statement cannot be confirmed. It is to be assumed
that the function v_setrgb is actually meant here; however the passing
of parameters is somewhat different.
|
| Group: |
Superior attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_setrgb vs_color vswr_mode
|
| Name: |
»Override gray level«
|
| Opcode: |
133
|
| Syntax: |
void vs_grayoverride ( int16_t handle, int16_t grayval );
|
| Description: |
The call vs_grayoverride overrides the grey level specified
with the vsf_style call patterns 2,1 through 2,8. The application
should specify the closest index in the normal fill pattern set and
follow it with a vs_grayoverride call to "fine-tune" that
gray level on devices that support such fine tuning. This call is
currently implemented in the PostScript driver.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| grayval |
Grey value in tenths of a percent
0 White
1000 Black
|
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
GEM/3 Release 3.1
|
| Group: |
Superior attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»PostScript halftoning« - Set PostScript halftoning.
|
| Opcode: |
5 (Escape 32)
|
| Syntax: |
void v_ps_halftone( int16_t handle, int16_t index, int16_t
angle, int16_t frequency );
|
| Description: |
The call v_ps_halftone controls the parameters for PostScript
halftoning. It provides direct access to analogous PostScript language
parameters. It is implemented only for the PostScript driver.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| index |
Halftone type:
0: Dot screen
1: Line screen
2: Ellipse screen
3: Custom (user-defined)
|
| angle |
Hallftone screen angle
|
| frequency |
Hallftone screen frequency
|
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
GEM/3 Release 3.1
|
| Group: |
Superior attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set colour representation« - Set colour intensity.
|
| Opcode: |
138
|
| Syntax: |
void v_setrgb( int16_t handle, int16_t type, int16_t r, int16_t
g, int16_t b );
|
| Description: |
The call v_setrgb selects the colour intensity of the
individual colour registers. The following apply:
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| type |
0: Text colour
1: Fill colour
2: Line colour
3: Marker colour
|
| r |
Red portion in tenths of a percent
|
| g |
Green portion in tenths of a percent
|
| b |
Blue portion in tenths of a percent
|
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
NVDI 5.00 onwards.
This is allegedly an old GEM/3 function. However such a
function could not be found until now.
|
| Group: |
Superior attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding
|
| Name: |
»Set colour representation« - Set the colour or intensity.
|
| Opcode: |
5 (Escape 18500)
|
| Syntax: |
void v_setrgbi( int16_t handle, int16_t primtype, int16_t r,
int16_t g, int16_t b, int16_t i );
|
| Description: |
The call v_setrgbi overrides a previously set colour
specification with an RGB triple (for colour devices) or intensity
(for monochrome devices). This call is currently implemented only for
the PostScript driver.
| Parameter |
Meaning
|
| |
|
| handle |
Workstation identifier
|
| primtype |
Primitive type:
17: Line
20: Marker
22: Text
25: Fill
|
| r |
Red portion in tenths of a percent
|
| g |
Green portion in tenths of a percent
|
| b |
Blue portion in tenths of a percent
|
| i |
Intensity
|
|
| Return value: |
The function does not return a result.
|
| Availability: |
GEM/3 Release 3.1
|
| Group: |
Superior attributes
|
| See also: |
Binding v_setrgb
|
| C: |
void v_setrgbi( int16_t handle, int16_t primtype, int16_t r,
int16_t g, int16_t b, int16_t i );
|
| Binding: |
void v_setrgbi( int16_t handle, int16_t primtype,
int16_t r, int16_t g, int16_t b, int16_t i )
{
intin[0] = primtype;
intin[1] = r;
intin[2] = g;
intin[3] = b;
intin[4] = i;
contrl[0] = 5;
contrl[1] = 0;
contrl[3] = 5;
contrl[5] = 18500;
contrl[6] = handle;
vdi ();
}
|
| GEM-Arrays: |
|

 VDI
VDI
 VDI bindings
VDI bindings
 Output functions
Output functions


